What is the impact of various water savings strategies on a large scale mixed used (residential, office, retails) building located in Shanghai China?
Olivier Brouard
Skidmore, Owings, and Merrill LLP
- Olivier Brouard, Sustainability Engineering Team Leader - Harshul Singhal, Building Performance Analyst - Christine Tiffin, Sustainability Design Specialist
Project Information
Floor plate area, user gender count, program use type, gallons of water consumption per year
gallons of water
1,000,000
3A
- Office
office, residential, retails
SIMULATION PROCESS SECTION
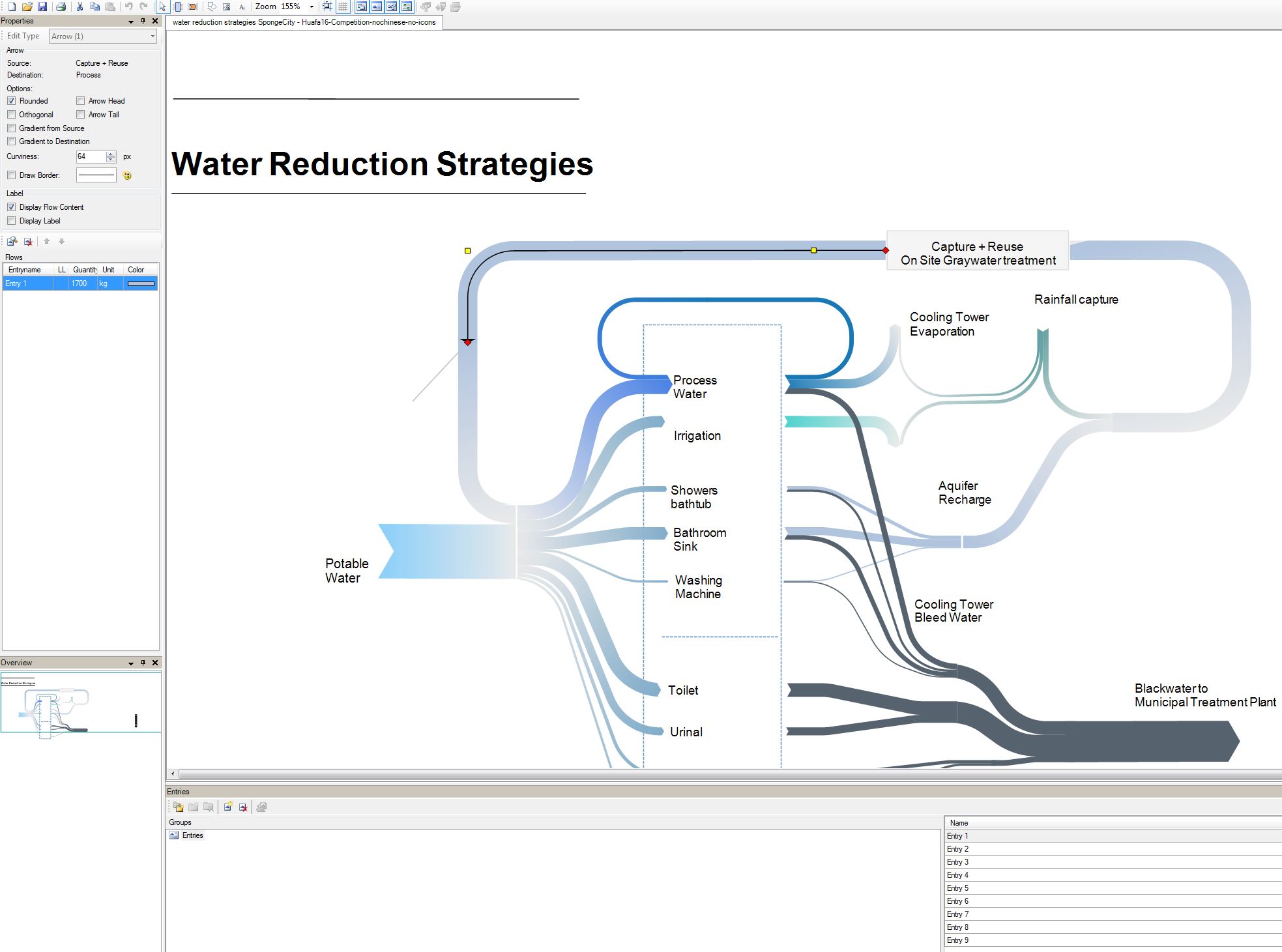
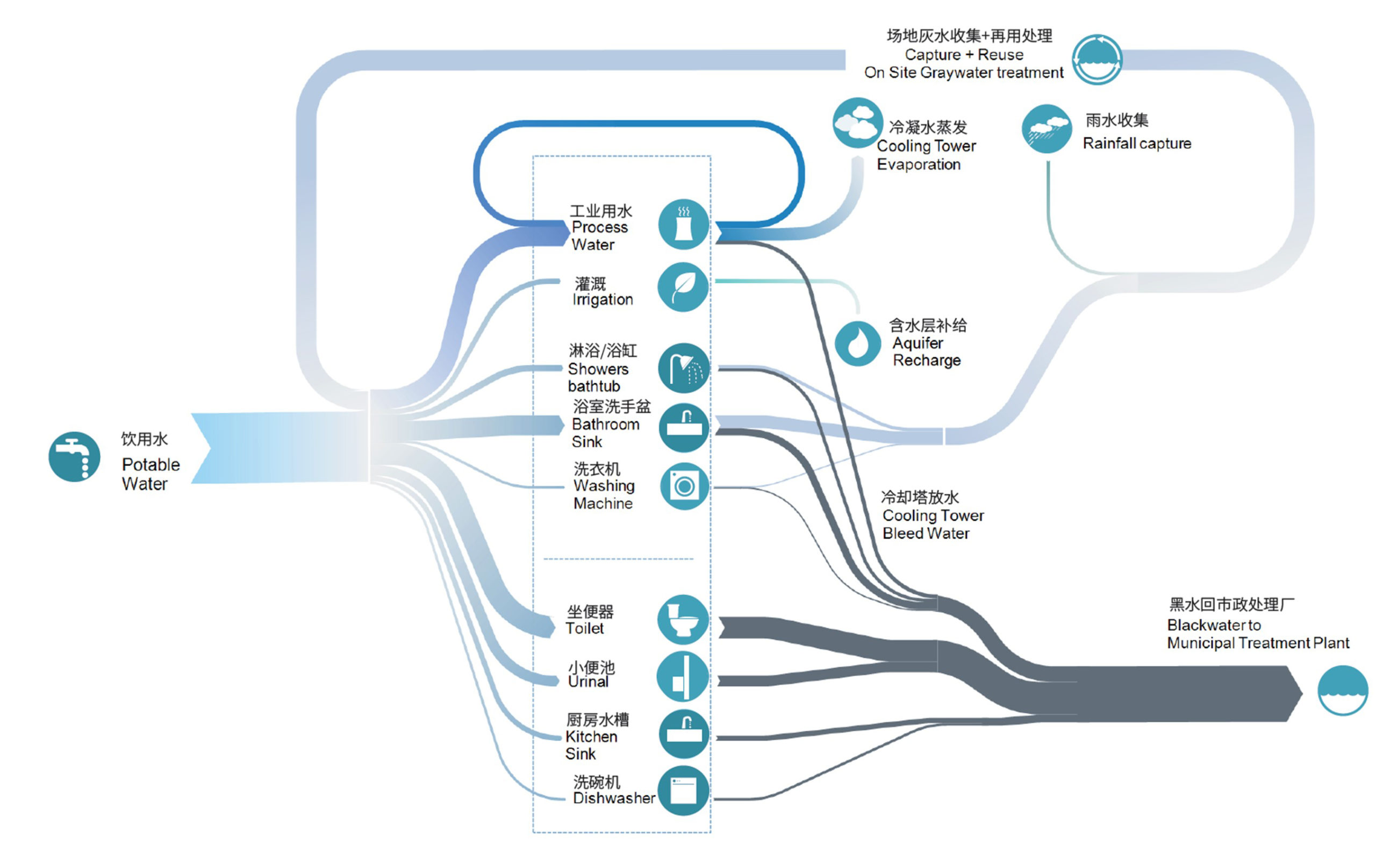
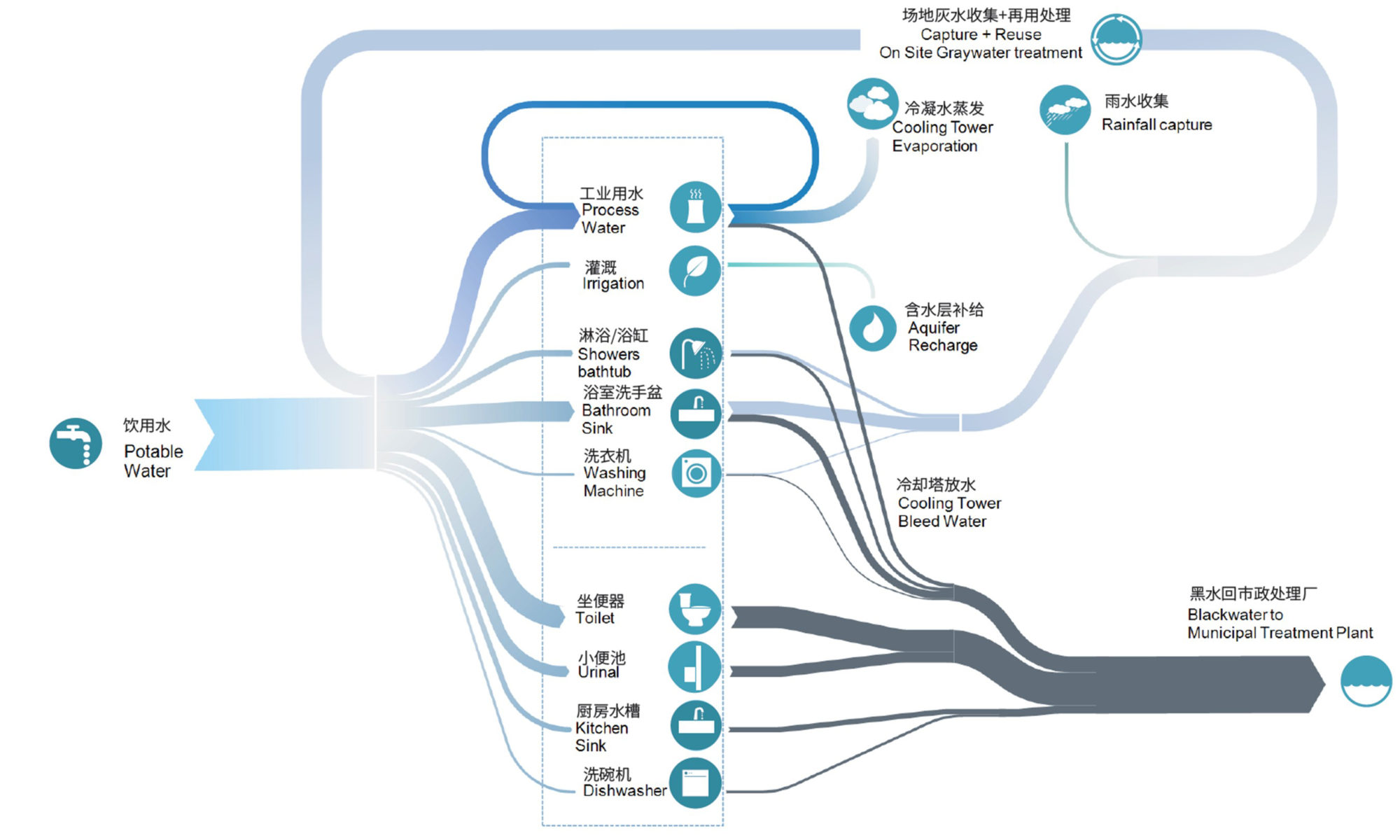
How to address visually the sponge city requirements in Shanghai, China, with various water reduction strategies through the following measures: - high-efficiency plumbing fixtures - no potable water use for plant irrigation - greywater recycling - condensate recovery - rainwater harvesting at roof level - permeable surfaces, bioswales
- Architect - Internal Sustainability Personnel
- OpenStudio + Eplus
- EnergyPlus
- Conceptual Design
The simulation was integrated at an early design conceptual phase as part of a competition. It was shown to the team during a meeting.
The simulation analysis followed best practices to reduce water savings through reduction, optimization, collection (green roof), on-site treatment and reuse (greywater). All the numbers were manually calculated using the LEED calculations. Some water consumption inputs came from the energy modeling outputs of the water system. The water rain collection metric came from the local weather file. The evaporation through the cooling tower came from the MEP team.
The tool used is "E-sankey" to create sankey diagrams. Not listed on the list above.
Adding a water story to the project statio competition would be a suggestion.